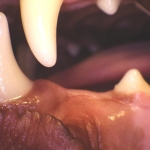
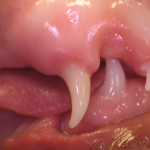
Dental occlusion is how the upper and lower jaws and teeth meet together when the mouth is closed.
Dogs and cats are to have a scissor bite.
We do not want abnormal tooth on tooth contact nor do we want tooth to soft tissue contact.
If there are skeletal abnormalities and/or if there are misaligned teeth, then the pet may suffer the consequences.
In order to identify abnormal, we must be able to recognize normal. These photos are taken from the AVDC website:
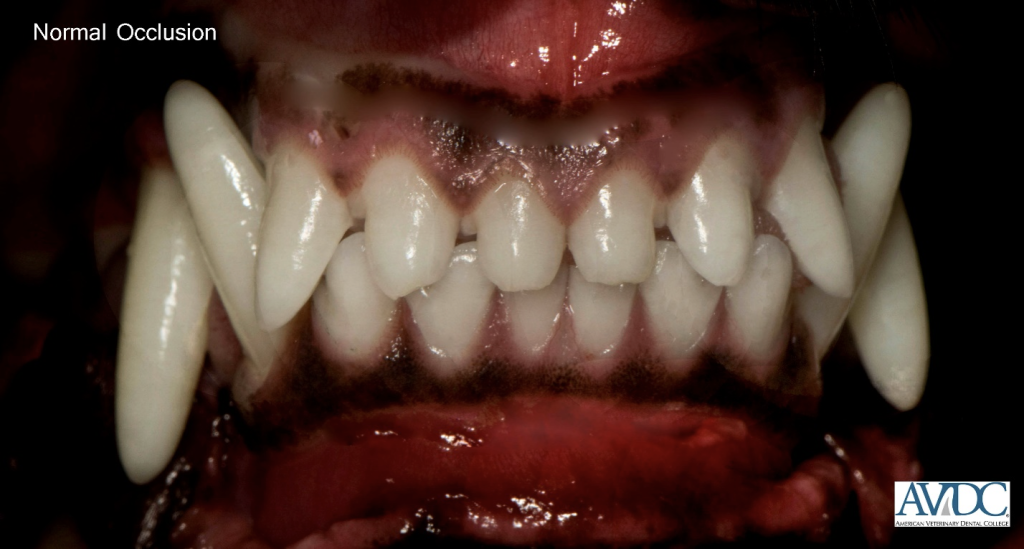
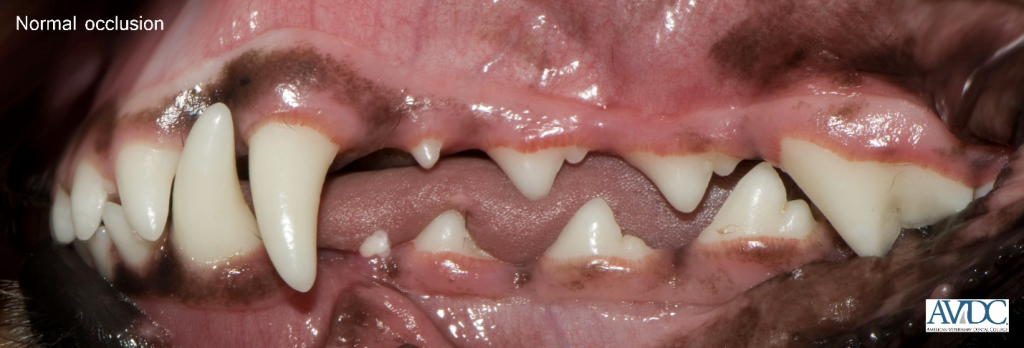
In a perfect world, all of our animals would have great genetics and perfectly normal occlusions. A normal occlusion requires the upper and lower jaws to be the appropriate length in relation to each other. In the dog, when the mouth is closed, the mandibular incisors should be just behind the upper incisors such that their cusps contact the cingulum of the maxillary incisor teeth.
The mandibular canine tooth is to be on an incline and sit in the interdental space between the upper maxillary third incisor and the canine tooth. The maxillary and mandibular premolar teeth should not touch each other and they are each situated that their crown sits in the interdental space to the corresponding opposing premolar teeth. The lower arches (jaws) are slightly more narrow than the upper arches (jaws). The mesial portion of the maxillary fourth premolar crown is buccal to the lower fourth premolar and lower first molar teeth.
Here are some photos of pets that I have seen with malocclusion. As you look at these, think of three consequences that these malocclusions have on the pet.
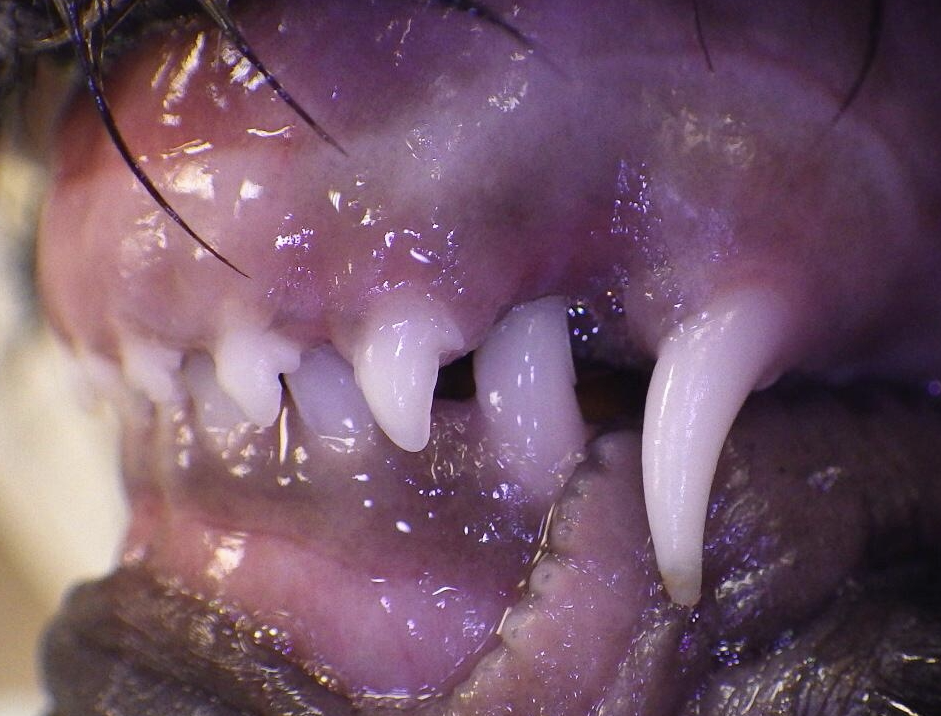
11 week old puppy with a
Class 1 Malocclusion
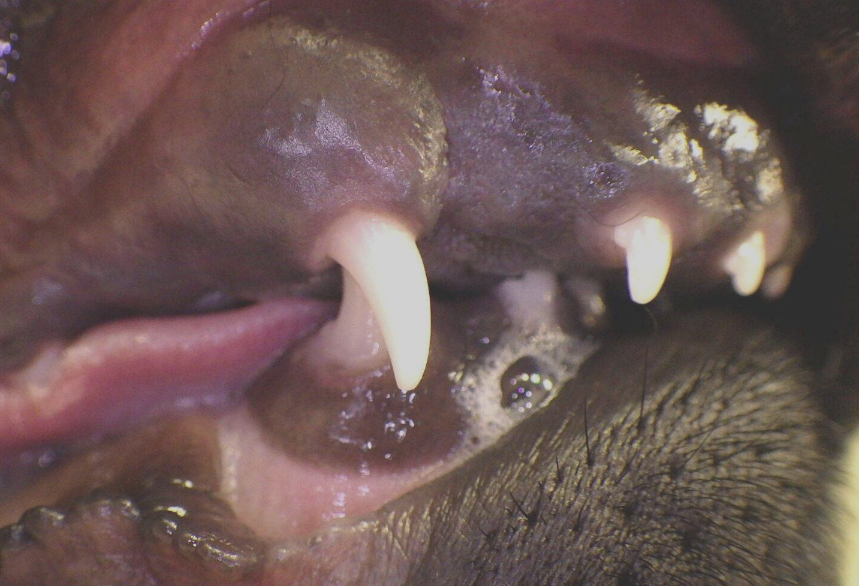
10 week old puppy with a
Class 2 Malocclusion
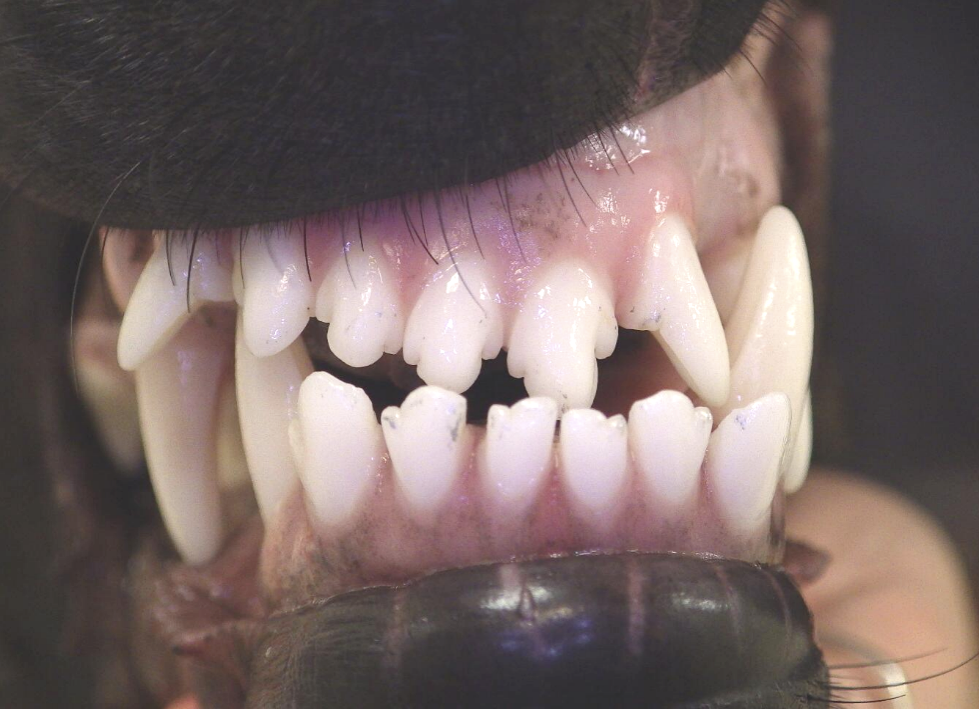
11 month old dog with a
Class 4 Malocclusion
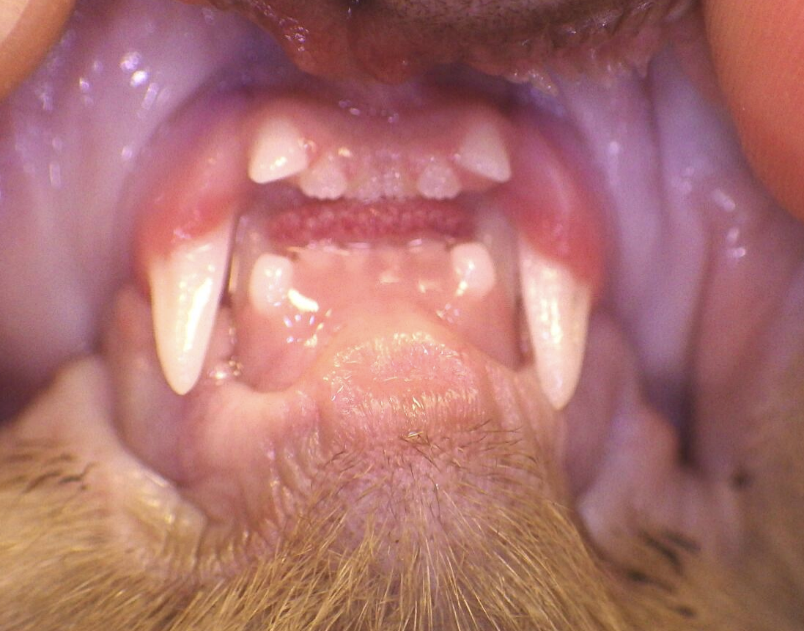
6 month old kitten with a
Class 2 Malocclusion
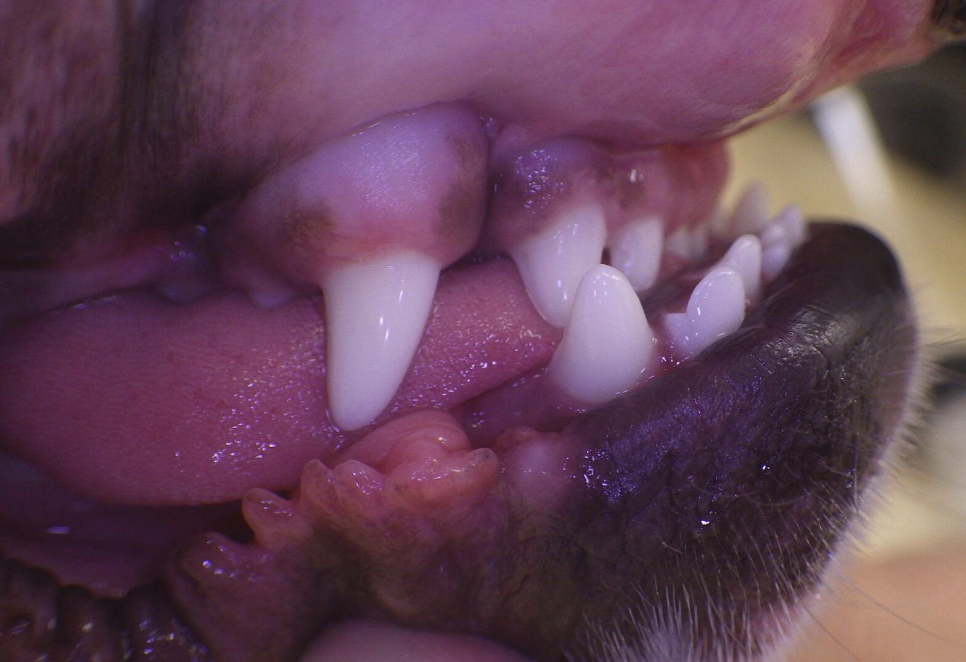
7 month old dog with a
Class 3 Malocclusion
So what three problems/consequences arise from having a malocclusion?
- Pain
- Infection
- They can Impede the proper growth of the bones and/or the eruption of certain teeth
Treatment is required based on the type and severity of the malocclusion. Treatment may include: selective extraction of teeth; orthodontic movement of teeth; crown reduction and vital pulp therapy.
Sometimes only one procedure is required and in some, multiple procedures under general anesthetic will be required.